Bifenthrin — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/08/2017 / By Michelle Simmons
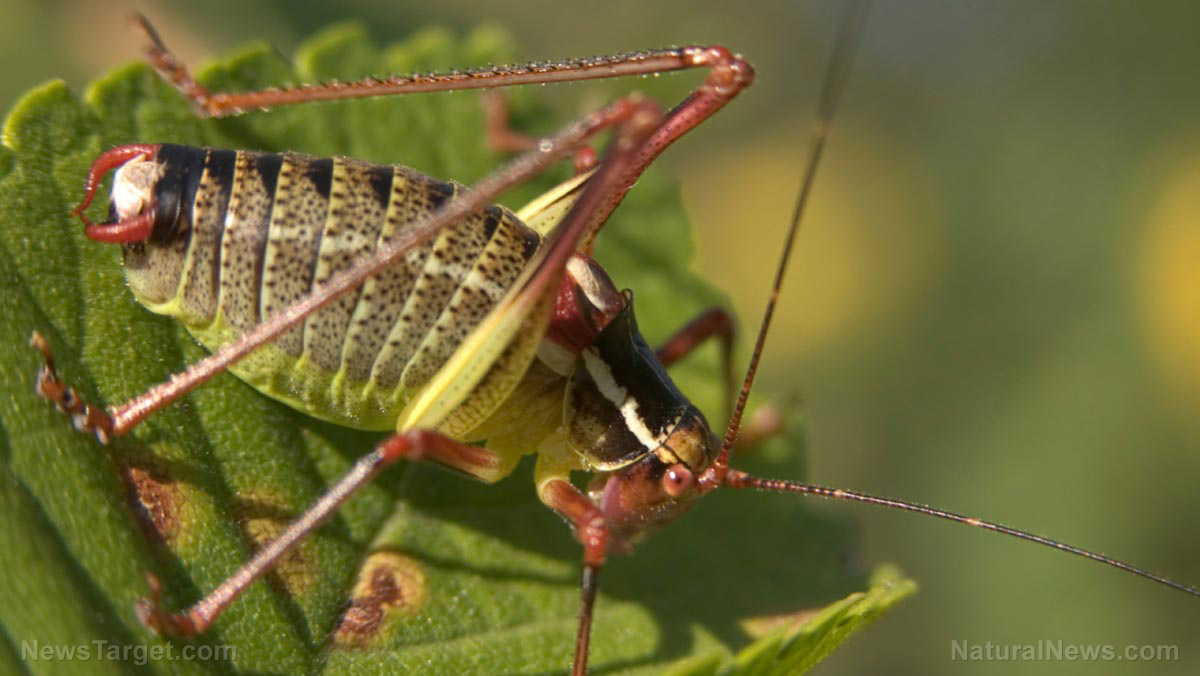

Bifenthrin is an insecticide that belongs to the pyrethroid group used against pests, such as fire ants, blue grass weevil, army worms, cut worms, centipedes, crickets, earwigs, millipedes, sowbugs, mole crickets, ticks, fleas, and grasshoppers. It is usually applied on non-cropped areas, such as lawns, athletic fields, ornamentals, residences, and commercial buildings. It works by interfering the functions of the insect’s nervous system when they eat or touch it, causing paralysis. Bifenthrin has the molecular formula of C23H22ClF3O2.
List of known side effects
A person could be exposed to bifenthrin if touched, ingested, or inhaled. When the chemical gets on the skin, bifenthrin can cause tingling, itching, burning, or numbness on the affected area. When inhaled, it can irritate the nose, throat, and lungs. Moreover, when large amounts of bifenthrin are ingested, it can cause sore throat, nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting almost immediately. Bifenthrin is also classified as a possible human carcinogen by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Bifenthrin can be poisonous to humans. Since it is a pyrethroid compound, it has similar symptoms of poisoning with other pyrethroid compounds. These include irritation of the skin and eyes, irritability to sound or touch, abnormal facial sensation, sensation of prickling, tingling, or creeping on skin, numbness, headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive salivation, and fatigue. In severe cases of bifenthrin poisoning, it may cause fluid in the lungs and muscle twitching.
For its environmental side effects, the chemical can bind to soil and can potentially contaminate surface waters through runoff. It is extremely toxic to the aquatic environment and bees.
Body systems affected by bifenthrin
The body systems negatively affected by bifenthrin include the integumentary, ocular, respiratory, nervous, digestive, excretory, and muscular systesms.
Items that can contain bifenthrin
Some of the trade names for products that contain acephate include Talstar, Bifenthrine, Brigade, Capture, FMC 54800, OMS3024, Torant (with Clofentezine), Zipak (with Amitraz), Gala 10 EC, Gyro, Starion Flo, Talstar Flo, and Talstar 8 SC. Products that contain bifenthrin come in different forms, such as sprays, granules, and aerosols.
How to avoid bifenthrin
Exposure to bifenthrin can be limited by reading the product label and following all of the directions. In addition, refrain from smoking, eating, or drinking without washing hands after using a product that contains the chemical.
Where to learn more
- Super bedbugs now emerging everywhere thanks to global travelers who carry the pests at the speed of jet travel
- New #1 Fruit Tops 2016 “Dirty Dozen” List of EWG’s Most Toxic
- Denmark discovers an alarmingly high concentration of pesticide poisoning in their population – school children are especially vulnerable
- Lab analysis shows strawberries are contaminated with 20 different pesticides, majority of which cause cancer in humans
- Commonly used insecticides impair child brain development even at low exposure levels
Summary
Bifenthrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, is used to control pests, including fire ants, blue grass weevil, army worms, cut worms, centipedes, crickets, earwigs, millipedes, sowbugs, mole crickets, ticks, fleas, and grasshoppers, on non-cropped areas, such as lawns, athletic fields, ornamentals, residences, and commercial buildings.
Bifenthrin can be poisonous to humans with symptoms of irritation of the skin and eyes, irritability to sound or touch, abnormal facial sensation, sensation of prickling, tingling, or creeping on skin, numbness, headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive salivation, and fatigue.
In severe cases of bifenthrin poisoning, it may cause fluid in the lungs and muscle twitching.
Bifenthrin can possibly cause cancer to humans.
Bifenthrin can bind to soil and can potentially contaminate surface waters through runoff.
Bifenthrin is extremely toxic to the aquatic environment and bees.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Bifenthrin