Chloridazon – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/08/2017 / By Rita Winters
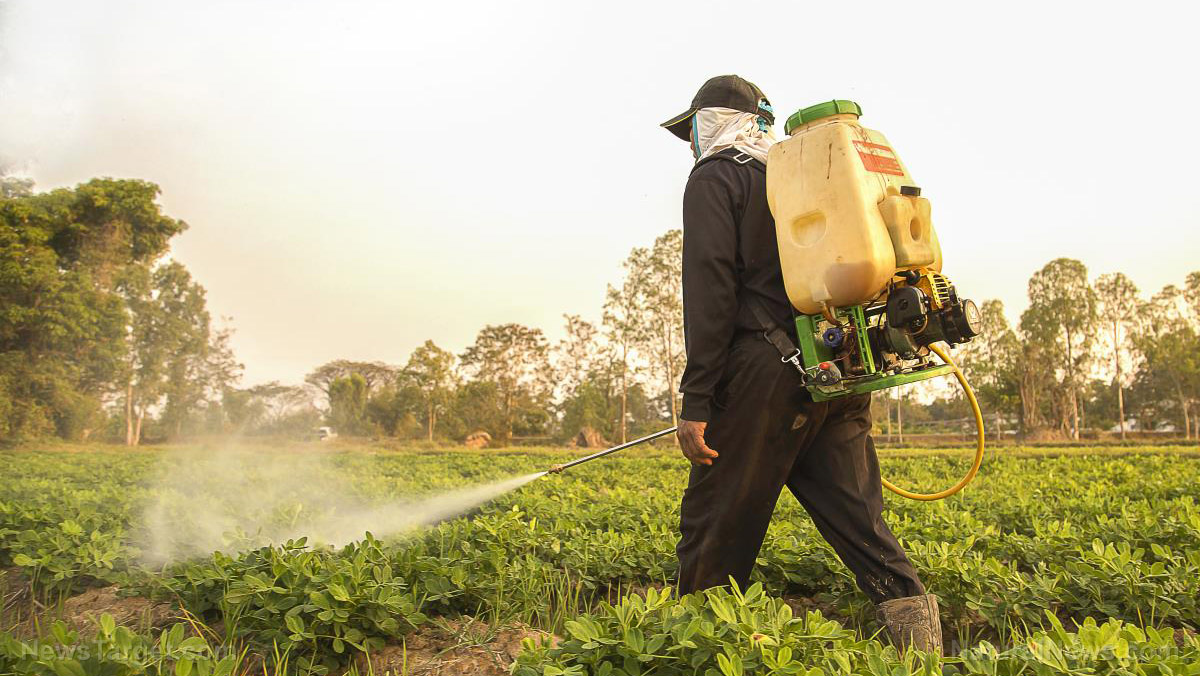

Chloridazon is a colorless and odorless chemical compound used in herbicide formulations. It targets broad-leaf and grass weeds including black grass, canary grass and wild oats. Chloridazon is a selective systemic herbicide that is rapidly absorbed by the roots of plants it is applied to, and travels to the stem to all the plants’ parts. It can be applied before planting a crop, before it emerges or after emergence of seedling. Chloridazon is often used with a combination of other herbicides.
Some names and synonyms of chloridazon include Chloridazon; CAS 1698-60-8; 5-Amino-4-chloro-2-phenylpyridazin-3(2H)-one; PYRAZON; Chloridazone; Curbetan; EC 216-920-2; chlordiazon; 3(2h)-pyridazinone, 5-amino-4-chloro; and Pyramine.
Like most herbicides, chloridazon may potentially be fatal if inhaled or ingested in large amounts or from constant exposure.

List of known side effects
Chloridazon is an herbicide that may cause negative side effects in humans. Poisoning may occur via inhalation, ingestion or skin contact. It is very toxic to aquatic life forms with long lasting effects, and may also be toxic to birds and mammals.
Laboratory tests on animals show that chloridazon may cause skin irritation, dermatitis, rashes and other dermal disorders. Eye irritation is also possible if the vapors, aerosols or dust gets in the eye. It may also cause mutagenic effects such as chromosome aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges in lymphocytes.
Body systems affected by chloridazon
Chloridazon highly affects the skin, the eyes and blood stream when inhaled, ingested or when skin or eye contact happens.
Further studies are needed in order to classify chloridazon in the teratogenic and carcinogenic aspects.
Items that may contain chloridazon
There are only 16 items registered for use in the U.S. that contain chloridazon, most of which have already been cancelled. Only two products have the only active registrations: Pyramin df herbicide 7969-81 and Pyramin super herbicide 7969-108.
Some crops that may contain residues of chloridazon include sugar beets, fodder beets, red beets, mangels, onions, shallots, garlic and ornamentals.
How to avoid chloridazon
Chloridazon is a commercial agricultural pesticide; therefore farmers, mixers and applicators are at risk of exposure to it. It is essential that all personnel handling this herbicide must wear protective gear. This includes chemical gloves, boots, long-sleeved chemical suits, goggles and a full-face respirator. Do not use in enclosed places since chloridazon is a fire hazard and may increase the rate by which it may be inhaled. Untrained and unauthorized personnel must not handle or be in proximity of chloridazon products. Proper hygiene must also be observed after handling the chemical.
In case of exposure, follow the necessary first aid measures. If inhaled, transfer the victim immediately to an open area with fresh air, and have the victim stay in a resting position. In case of skin contact, wash the affected area of skin immediately with clean water and soap. If aerosols or sprays come in contact with the eye, flush out the affected part with clean, running water for at least 10 minutes. In case of ingestion, contact emergency medical services as soon as possible, or transport the victim to the nearest emergency department. Always contact a medical expert as soon as possible.
Where to learn more
- Scientists argue that the world needs more natural “biopesticides” rather than synthetic chemical pesticides
- Poison.news
- Chemicals.news
- Pesticides.news
- Toxins.news
Summary
Chloridazon is a colorless and odorless chemical found in herbicides.
Chloridazon may leave residues on plants it is applied to.
Chloridazon may cause negative side effects in humans.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: chloridazon